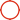
Blow molding machines and rotational molding machines, as two important pieces of equipment in plastic molding processing, both convert plastic raw materials into hollow products, but they differ significantly in working principles, application scopes, and product characteristics. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting appropriate production equipment.
In terms of working principles, blow molding machines adopt the "hollow blow molding" process. The process involves extruding molten plastic raw materials through an extruder to form a tubular parison. Then, the parison is placed in an open mold, and after the mold is closed, high-pressure air is injected into the parison, causing the plastic parison to expand and adhere to the inner wall of the mold. After cooling and setting, a hollow product consistent with the shape of the mold is obtained. This process is similar to blow molding with a balloon, relying on the combined action of the external mold and internal air pressure to determine the product shape.
Rotational molding machines, on the other hand, use the "rotational molding" process, whose workflow is essentially different from that of blow molding machines. Firstly, a fixed amount of plastic powder or granular raw materials is added into a closed mold. Then, the mold rotates slowly around two mutually perpendicular axes while being heated. Under the dual action of heating and rotation, the raw materials gradually melt and uniformly adhere to the inner wall of the mold, forming a thin layer consistent with the shape of the mold cavity. After that, heating is stopped, and the mold continues to rotate until the product is cooled and set. Finally, the mold is opened to take out the product. Rotational molding is more like letting the molten raw materials "spread" over the inner wall of the mold through gravity and centrifugal force, and the entire process does not require high-pressure air assistance.
In terms of application scope, blow molding machines are more suitable for producing small and medium-sized hollow products with relatively simple structures, such as plastic bottles, barrels, and fuel tanks. They have an efficiency advantage especially in mass-producing standardized products, with a short production cycle, which can meet the demand for rapid supply. Rotational molding machines, however, excel in producing large, extra-large, or complex-shaped hollow products, such as large liquid storage tanks, yacht hulls, and children's amusement facilities. They have high requirements for the uniformity of product wall thickness and can achieve integral molding, reducing quality risks caused by splicing. However, the production cycle is relatively long, making them more suitable for small-batch, customized production.
In terms of product characteristics, blow molded products have high precision in wall thickness control, good surface finish, and balanced mechanical properties, suitable for withstanding a certain internal pressure. Rotational molded products have a more uniform wall thickness distribution, especially for corners, curved surfaces, and other parts of large products, which can avoid uneven wall thickness that may occur in blow molding. Moreover, because the raw materials are fully melted and fused in the mold, the products have stronger integrity and impact resistance, suitable for long-term outdoor use or withstanding complex external forces.
To sum up, blow molding machines and rotational molding machines have their own focuses in molding principles, application scenarios, and product performance. When selecting, factors such as product size, shape, production volume requirements, and usage environment should be comprehensively considered to achieve the optimal balance between production efficiency and product quality.
Differences Between Blow Molding Machines and Rotational Molding Machines
August 21, 2025